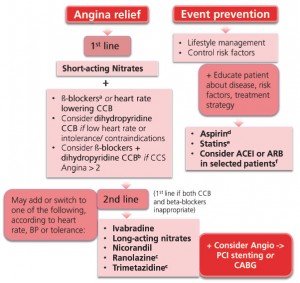
Optimal medical treatment indicates at least one drug for angina/ischaemia relief plus drugs for event prevention (see algorithm below for fist line and second line therapies [adapted from ESC guidelines])1
Download PDF: MIMS Ireland – SUPP – ESC guidelines- algorithm and tables
Click to enlarge
ACEI = angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor; ARB = angiotensin II receptor blocker; CABG = coronary artery bypass graft; CCB = calcium channel blockers; CCS = Canadian Cardiovascular Society; DHP = dihydropyridine; PCI = percutaneous coronary intervention.
a: ß-blockers should be considered in asymptomatic patients with large areas of ischaemia (>10%). In patients with vasospastic angina, CCBs and nitrates should be considered and ß-blockers avoided.
b: The combination of a heart rate lowering CCB with a ß -blocker is not advised.
c: Data for diabetics.
d: Low dose aspirin daily is recommended in all SCAD patients; if intolerance, consider clopidogrel.
e: Statins are recommended in all SCAD patients.
f: It is recommended to use ACEIs (or ARBs) if presence of other conditions (e.g. heart failure, hypertension or diabetes).
Table 1 indicates the main side-effects, contra-indications and major drug-drug interactions for each class of anti-ischaemic drugs.
Table 2 offers recommendations on the optimal Use on nitrates in stable coronary artery disease.
Reference: 1- [Adapted from] 2013 ESC guidelines on the management of stable coronary artery disease. Eur Heart J. 2013 Oct;34(38):2949-3003. MIMS Ireland Copyright®